Introduction:
Machine guarding is an essential safety measure that protects workers from hazardous moving parts of machinery. Failure to properly guard machinery can lead to serious injuries, including amputations, lacerations, and fractures. In this toolbox talk, we will discuss the importance of machine guarding, the types of guards used, and the responsibilities of employers and employees in ensuring machine safety.
Importance of Machine Guarding:
Machines are used in various industries, and they have moving parts that can cause severe injuries if not properly guarded. Machine guarding is critical to preventing accidents and ensuring workplace safety. OSHA estimates that lack of proper machine guarding results in over 18,000 injuries and 800 fatalities every year. Properly guarding machinery can help prevent accidents and save lives.
Types of Machine Guards:
There are several types of machine guards that can be used to protect workers from hazardous machinery:
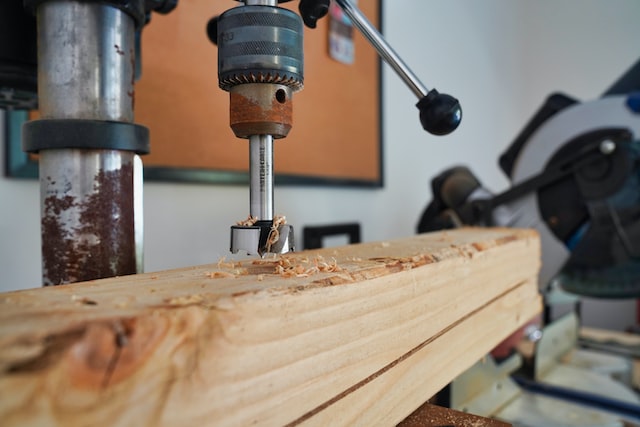
1. Fixed Guards: Fixed guards are the most common type of machine guards. They are permanently attached to the machine and prevent access to hazardous areas. Fixed guards are typically used for machines with a fixed operating cycle.
2. Interlocked Guards: Interlocked guards are designed to shut off or disengage the machine when the guard is removed or opened. This type of guard is commonly used for machines that have a high risk of injury, such as power presses and robotic equipment.
3. Adjustable Guards: Adjustable guards are designed to be moved to accommodate different sizes of materials or parts. They are typically used for machines that process different sizes of materials, such as saws and shears.
4. Self-Adjusting Guards: Self-adjusting guards move with the machinery to provide protection at all times. They are typically used for machines that have a constant change in the size of materials, such as conveyors and printing presses.
5. Barrier Guards: Barrier guards are used to physically separate workers from hazardous areas. They are typically used for machines that are difficult to guard using other types of guards, such as welding machines and lathes.
Responsibilities of Employers and Employees:
Employers and employees both have responsibilities to ensure machine safety in the workplace.
Employer Responsibilities:
- Employers have a legal and ethical responsibility to provide a safe working environment for their employees. They must:
- Identify and assess potential machine hazards: Employers must identify and assess the potential hazards associated with the machinery in their workplace.
- Implement appropriate machine guards: Employers must select and implement the appropriate machine guards for the machines in their workplace.
- Train employees: Employers must provide training to employees on the proper use of machine guards and the hazards associated with the machines they will be operating.
- Inspect machine guards regularly: Employers must regularly inspect machine guards to ensure they are in proper working order.
Employee Responsibilities:
- Employees also have a responsibility to ensure their own safety and the safety of their colleagues. They must:
- Follow safe work practices: Employees must follow all safe work practices and procedures when operating machinery.
- Use machine guards properly: Employees must use machine guards properly and not remove or disable them.
- Report hazards: Employees must report any machine hazards or malfunctions to their supervisor immediately.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, machine guarding is an essential safety measure that protects workers from hazardous moving parts of machinery. Properly guarding machinery can prevent accidents and save lives. There are several types of machine guards that can be used to protect workers, and employers and employees both have responsibilities to ensure machine safety in the workplace. By following safe work practices and using appropriate machine guards, we can ensure a safer working environment for everyone.