Evaluation & Selection of Fall Protection
Introduction:
We have come a long way in the development, education, and implementation of Fall Prevention & Fall Protection. Even with the progress that has been made, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), in 2021 Fatal Workplace Incidents rose 8.9% from 2020 and accounted for 5,190 deaths. What contributes to workplace injuries/fatalities? Below is a list of contributing factors as it relates to the occurrence of workplace injuries/fatalities.
- Identification and mitigation of hazards
- Selection of Personal Protective Equipment
- Employee Training
- Failure in Equipment
- Human Nature
Identification of Fall Hazards
As you evaluate your workplace/job site, identify the potential fall hazards that could result in an injury or incident. Common fall hazards can include:
- Working from ladders/temporary work platforms such as aerial lifts and man lifts
- Leading edges
- Uneven work surfaces
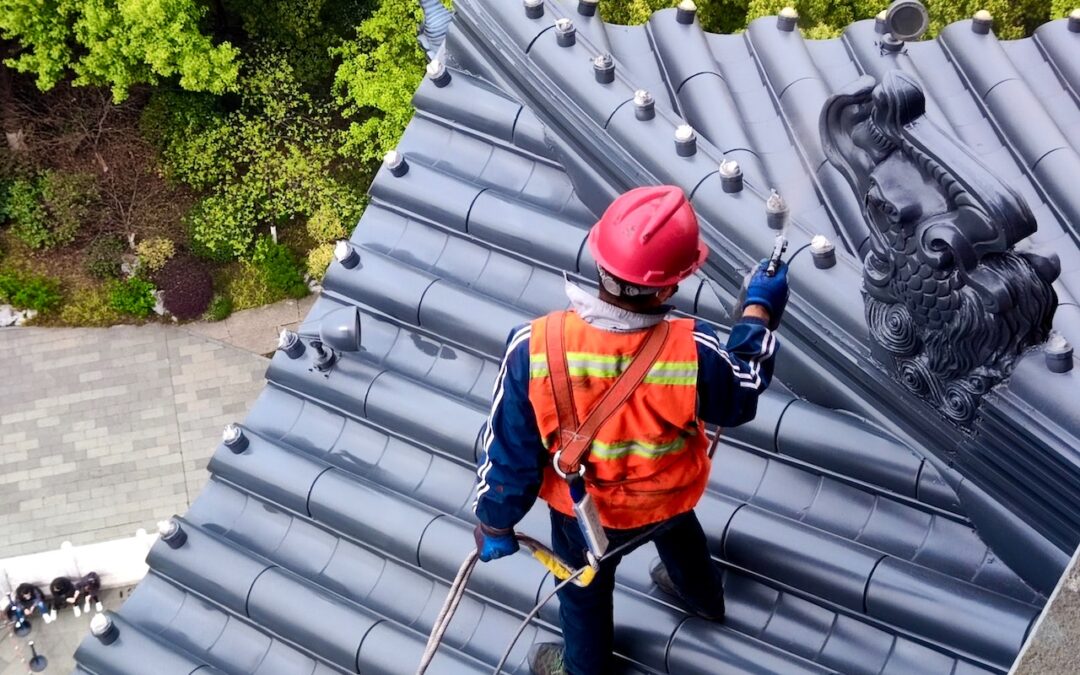
- Rooftops
- Open holes/trenches/excavations
- Catwalks
- Slippery surfaces
- etc
After identifying all fall hazards the next step is to prevent falls by eliminating the fall hazards or making it less likely a fall will occur (through mitigation methods). Understanding your obligations as a Safety Professional/Employer, there are different requirements set forth by OSHA that dictate how fall hazards are addressed. It is equally important to understand what working heights employees must be protected at for elevated work. Employers in General Industry (where CFR 1910 applies), must protect employees from all fall hazards and institute fall protection when working at heights 4ft or greater where fall hazards are present. In Construction (where CFR 1926 applies), employees must be protected at working heights of 6ft or greater.
Prevention of Fall Hazards
Following the Hierarchy of Controls, the best way to prevent falls, is to eliminate the fall hazard all together. Falls hazards can be eliminated through the implementation of guard rails, fall restraint systems, hole covers and other passive fall protection controls. It is important to remember, that not all fall hazards can be eliminated. Some workplaces conditions will necessitate that certain conditions are left unchanged, for work to be performed.
Administrative Controls
If employers are unable to eliminate fall hazards through the use of engineering controls, administrative controls must be implemented. Administrative controls bring awareness to hazards and can include safety signage, safety training, company operating procedures, use of permits and by creating work plans such as phasing the order in which work will be completed. Keep in mind, these administrative controls must be implemented before the use of Personal Protective Equipment.
Personal Protective Equipment PPE
If fall hazards cannot be eliminated, and administrative controls still do not reasonably prevent falls from occurring, personal protective equipment must be utilized. The most common form of PPE for fall protection is the use of Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS).
Personal Fall Arrest Systems are designed to arrest the worker in the event of a fall, and minimize the impact force that is placed on the worker. Personal Fall arrest systems include: anchorage points (existing or engineered), body harnesses, a connecting device, and a deceleration device.
Selection of Personal Fall Arrest Systems
The market is full of different styles and components that can be used to design your personal fall arrest system. So where do you start? You need to ensure that the systems you have in place will engage during a fall before the worker hits the ground. OSHA specifically has guidelines that state the system needs to engage within 3ft after a fall occurs. The anchorage point needs to be able to withstand 5,000lbs of free fall force. Body harnesses need to be fitted to the worker, fit comfortable, and displace the force in a manner that reduces impact on the worker.
Fall Protection Assessment
B42L offers free fall protection assessments. Our partnership with Gallaway Safety & Supply, allows us to come to your workplace, evaluate what you have in place, and provide options for you that best protect your workers. Our assessment will give you options for assigning fall protection, tracking it in the field, and how to properly inspect it for proper function.
Training on Fall Protection
After you have your fall protection selected and assigned, B42L will train your staff on the proper use, inspection, and storage of fall protection. Training on Fall Protection is an OSHA Top 10 Violation annually. Simply providing it does not meet the mark of compliance, and it does not ensure your staff will use it safely.
If you are interested in a fall protection assessment or fall protection demonstrations/training:
Call 412-216-9427 or email info@b42l.com